Functions
- accelerator_get_default_mod_mask() ModifierType
Gets the modifier mask.
The modifier mask determines which modifiers are considered significant for keyboard accelerators. This includes all keyboard modifiers except for
%GDK_LOCK_MASK.- Returns:
the modifier mask for accelerators
- accelerator_get_label(accelerator_key: int, accelerator_mods: ModifierType) str
Converts an accelerator keyval and modifier mask into a string which can be used to represent the accelerator to the user.
- Parameters:
accelerator_key – accelerator keyval
accelerator_mods – accelerator modifier mask
- Returns:
a newly-allocated string representing the accelerator
- accelerator_get_label_with_keycode(display: Display | None, accelerator_key: int, keycode: int, accelerator_mods: ModifierType) str
Converts an accelerator keyval and modifier mask into a string that can be displayed to the user.
The string may be translated.
This function is similar to
accelerator_get_label, but handling keycodes. This is only useful for system-level components, applications should useaccelerator_get_labelinstead.- Parameters:
display – a
GdkDisplayorNoneto use the default displayaccelerator_key – accelerator keyval
keycode – accelerator keycode
accelerator_mods – accelerator modifier mask
- Returns:
a newly-allocated string representing the accelerator
- accelerator_name(accelerator_key: int, accelerator_mods: ModifierType) str
Converts an accelerator keyval and modifier mask into a string parseable by
accelerator_parse().For example, if you pass in
%GDK_KEY_qand%GDK_CONTROL_MASK, this function returns<Control>q.If you need to display accelerators in the user interface, see
accelerator_get_label.- Parameters:
accelerator_key – accelerator keyval
accelerator_mods – accelerator modifier mask
- Returns:
a newly-allocated accelerator name
- accelerator_name_with_keycode(display: Display | None, accelerator_key: int, keycode: int, accelerator_mods: ModifierType) str
Converts an accelerator keyval and modifier mask into a string parseable by
accelerator_parse_with_keycode().This is similar to
accelerator_namebut handling keycodes. This is only useful for system-level components, applications should useaccelerator_nameinstead.- Parameters:
display – a
GdkDisplayorNoneto use the default displayaccelerator_key – accelerator keyval
keycode – accelerator keycode
accelerator_mods – accelerator modifier mask
- Returns:
a newly allocated accelerator name.
- accelerator_parse(accelerator: str) tuple[bool, int, ModifierType]
Parses a string representing an accelerator.
The format looks like “
<Control>a” or “<Shift><Alt>F1”.The parser is fairly liberal and allows lower or upper case, and also abbreviations such as “
<Ctl>” and “<Ctrl>”.Key names are parsed using
keyval_from_name. For character keys the name is not the symbol, but the lowercase name, e.g. one would use “<Ctrl>minus” instead of “<Ctrl>-”.Modifiers are enclosed in angular brackets
<>, and match theModifierTypemask:<Shift>forGDK_SHIFT_MASK<Ctrl>forGDK_CONTROL_MASK<Alt>forGDK_ALT_MASK<Meta>forGDK_META_MASK<Super>forGDK_SUPER_MASK<Hyper>forGDK_HYPER_MASK
If the parse operation fails,
accelerator_keyandaccelerator_modswill be set to 0 (zero).- Parameters:
accelerator – string representing an accelerator
- accelerator_parse_with_keycode(accelerator: str, display: Display | None = None) tuple[bool, int, list[int], ModifierType]
Parses a string representing an accelerator.
This is similar to
accelerator_parsebut handles keycodes as well. This is only useful for system-level components, applications should useaccelerator_parseinstead.If
accelerator_codesis given and the result stored in it is non-None, the result must be freed withfree().If a keycode is present in the accelerator and no
accelerator_codesis given, the parse will fail.If the parse fails,
accelerator_key,accelerator_modsandaccelerator_codeswill be set to 0 (zero).- Parameters:
accelerator – string representing an accelerator
display – the
GdkDisplayto look upaccelerator_codesin
- Returns:
Trueif parsing succeeded
- accelerator_valid(keyval: int, modifiers: ModifierType) bool
Determines whether a given keyval and modifier mask constitute a valid keyboard accelerator.
For example, the
%GDK_KEY_akeyval plus%GDK_CONTROL_MASKmark is valid, and matches the “Ctrl+a” accelerator. But, you can’t, for instance, use the%GDK_KEY_Control_Lkeyval as an accelerator.- Parameters:
keyval – a GDK keyval
modifiers – modifier mask
- Returns:
Trueif the accelerator is valid
- accessible_property_init_value(property: AccessibleProperty, value: Any) None
- Parameters:
property
value
- accessible_relation_init_value(relation: AccessibleRelation, value: Any) None
- Parameters:
relation
value
- accessible_state_init_value(state: AccessibleState, value: Any) None
- Parameters:
state
value
- check_version(required_major: int, required_minor: int, required_micro: int) str | None
Checks that the GTK library in use is compatible with the given version.
Generally you would pass in the constants
MAJOR_VERSION,MINOR_VERSION,MICRO_VERSIONas the three arguments to this function; that produces a check that the library in use is compatible with the version of GTK the application or module was compiled against.Compatibility is defined by two things: first the version of the running library is newer than the version
required_major.required_minor.``required_micro``. Second the running library must be binary compatible with the versionrequired_major.required_minor.``required_micro`` (same major version.)This function is primarily for GTK modules; the module can call this function to check that it wasn’t loaded into an incompatible version of GTK. However, such a check isn’t completely reliable, since the module may be linked against an old version of GTK and calling the old version of
check_version(), but still get loaded into an application using a newer version of GTK.- Parameters:
required_major – the required major version
required_minor – the required minor version
required_micro – the required micro version
- Returns:
Noneif the GTK library is compatible with the given version, or a string describing the version mismatch. The returned string is owned by GTK and should not be modified or freed.
- disable_setlocale() None
Prevents
initandinit_checkfrom automatically callingsetlocale (LC_ALL, "").You would want to use this function if you wanted to set the locale for your program to something other than the user’s locale, or if you wanted to set different values for different locale categories.
Most programs should not need to call this function.
- distribute_natural_allocation(extra_space: int, sizes: Sequence[RequestedSize]) int
Distributes
extra_spaceto childsizesby bringing smaller children up to natural size first.The remaining space will be added to the
minimum_sizemember of theGtkRequestedSizestruct. If all sizes reach their natural size then the remaining space is returned.- Parameters:
extra_space – Extra space to redistribute among children after subtracting minimum sizes and any child padding from the overall allocation
sizes – An array of structs with a client pointer and a minimum/natural size in the orientation of the allocation.
- Returns:
The remainder of
extra_spaceafter redistributing space tosizes.
- editable_delegate_get_property(object: Object, prop_id: int, value: Any, pspec: ParamSpec) bool
- Parameters:
object
prop_id
value
pspec
- editable_delegate_set_property(object: Object, prop_id: int, value: Any, pspec: ParamSpec) bool
- Parameters:
object
prop_id
value
pspec
- editable_install_properties(object_class: ObjectClass, first_prop: int) int
- Parameters:
object_class
first_prop
- enumerate_printers(func: Callable[[...], bool], wait: bool, *data: Any) None
Calls a function for all
GtkPrinter’s.If
funcreturnsTrue, the enumeration is stopped.- Parameters:
func – a function to call for each printer
wait – if
True, wait in a recursive mainloop until all printers are enumerated; otherwise return earlydata – user data to pass to
func
- get_binary_age() int
Returns the binary age as passed to
libtool.If
libtoolmeans nothing to you, don’t worry about it.- Returns:
the binary age of the GTK library
- get_debug_flags() DebugFlags
Returns the GTK debug flags that are currently active.
This function is intended for GTK modules that want to adjust their debug output based on GTK debug flags.
- Returns:
the GTK debug flags.
- get_default_language() Language
Returns the
PangoLanguagefor the default language currently in effect.Note that this can change over the life of an application.
The default language is derived from the current locale. It determines, for example, whether GTK uses the right-to-left or left-to-right text direction.
This function is equivalent to
get_default. See that function for details.- Returns:
the default language
- get_interface_age() int
Returns the interface age as passed to
libtool.If
libtoolmeans nothing to you, don’t worry about it.- Returns:
the interface age of the GTK library
- get_locale_direction() TextDirection
Get the direction of the current locale. This is the expected reading direction for text and UI.
This function depends on the current locale being set with setlocale() and will default to setting the
LTRdirection otherwise.NONEwill never be returned.GTK sets the default text direction according to the locale during
init(), and you should normally useget_direction()orget_default_direction()to obtain the current direction.This function is only needed rare cases when the locale is changed after GTK has already been initialized. In this case, you can use it to update the default text direction as follows:
``include`` <locale.h> static void update_locale (const char *new_locale) { setlocale (LC_ALL, new_locale); gtk_widget_set_default_direction (gtk_get_locale_direction ()); }
- Returns:
the direction of the current locale
- get_major_version() int
Returns the major version number of the GTK library.
For example, in GTK version 3.1.5 this is 3.
This function is in the library, so it represents the GTK library your code is running against. Contrast with the
MAJOR_VERSIONmacro, which represents the major version of the GTK headers you have included when compiling your code.- Returns:
the major version number of the GTK library
- get_micro_version() int
Returns the micro version number of the GTK library.
For example, in GTK version 3.1.5 this is 5.
This function is in the library, so it represents the GTK library your code is are running against. Contrast with the
MICRO_VERSIONmacro, which represents the micro version of the GTK headers you have included when compiling your code.- Returns:
the micro version number of the GTK library
- get_minor_version() int
Returns the minor version number of the GTK library.
For example, in GTK version 3.1.5 this is 1.
This function is in the library, so it represents the GTK library your code is are running against. Contrast with the
MINOR_VERSIONmacro, which represents the minor version of the GTK headers you have included when compiling your code.- Returns:
the minor version number of the GTK library
- hsv_to_rgb(h: float, s: float, v: float) tuple[float, float, float]
Converts a color from HSV space to RGB.
Input values must be in the [0.0, 1.0] range; output values will be in the same range.
- Parameters:
h – Hue
s – Saturation
v – Value
- init() None
Call this function before using any other GTK functions in your GUI applications. It will initialize everything needed to operate the toolkit.
If you are using
GtkApplication, you usually don’t have to call this function; theGApplication::startuphandler does it for you. Though, if you are using GApplication methods that will be invoked beforestartup, such aslocal_command_line, you may need to initialize stuff explicitly.This function will terminate your program if it was unable to initialize the windowing system for some reason. If you want your program to fall back to a textual interface, call
init_checkinstead.GTK calls
signal (SIGPIPE, SIG_IGN)during initialization, to ignore SIGPIPE signals, since these are almost never wanted in graphical applications. If you do need to handle SIGPIPE for some reason, reset the handler afterinit(), but notice that other libraries (e.g. libdbus or gvfs) might do similar things.
- init_check() bool
This function does the same work as
init()with only a single change: It does not terminate the program if the windowing system can’t be initialized. Instead it returnsFalseon failure.This way the application can fall back to some other means of communication with the user - for example a curses or command line interface.
- Returns:
Trueif the windowing system has been successfully initialized,Falseotherwise
- is_initialized() bool
Use this function to check if GTK has been initialized.
See
init.- Returns:
the initialization status
- param_spec_expression(name: str, nick: str, blurb: str, flags: ParamFlags) ParamSpec
Creates a new
GParamSpecinstance for a property holding aGtkExpression.See
:func:`~gi.repository.GObject.GObject.ParamSpec.internal`for details on the property strings.- Parameters:
name – canonical name of the property
nick – a user-readable name for the property
blurb – a user-readable description of the property
flags – flags for the property
- Returns:
a newly created property specification
- print_run_page_setup_dialog(parent: Window | None, page_setup: PageSetup | None, settings: PrintSettings) PageSetup
Runs a page setup dialog, letting the user modify the values from
page_setup. If the user cancels the dialog, the returnedGtkPageSetupis identical to the passed inpage_setup, otherwise it contains the modifications done in the dialog.Note that this function may use a recursive mainloop to show the page setup dialog. See
print_run_page_setup_dialog_async()if this is a problem.- Parameters:
parent – transient parent
page_setup – an existing
GtkPageSetupsettings – a
GtkPrintSettings
- Returns:
a new
GtkPageSetup
- print_run_page_setup_dialog_async(parent: Window | None, page_setup: PageSetup | None, settings: PrintSettings, done_cb: Callable[[...], None], *data: Any) None
Runs a page setup dialog, letting the user modify the values from
page_setup.In contrast to
print_run_page_setup_dialog(), this function returns after showing the page setup dialog on platforms that support this, and callsdone_cbfrom a signal handler for the ::response signal of the dialog.- Parameters:
parent – transient parent
page_setup – an existing
GtkPageSetupsettings – a
GtkPrintSettingsdone_cb – a function to call when the user saves the modified page setup
data – user data to pass to
done_cb
- render_activity(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders an activity indicator (such as in
GtkSpinner). The stateCHECKEDdetermines whether there is activity going on.Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_arrow(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, angle: float, x: float, y: float, size: float) None
Renders an arrow pointing to
angle.Typical arrow rendering at 0, 1⁄2 π;, π; and 3⁄2 π:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tangle – arrow angle from 0 to 2 *
``%G_PI``, being 0 the arrow pointing to the northx – X origin of the render area
y – Y origin of the render area
size – square side for render area
- render_background(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders the background of an element.
Typical background rendering, showing the effect of
background-image,border-widthandborder-radius:
Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_check(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders a checkmark (as in a
GtkCheckButton).The
CHECKEDstate determines whether the check is on or off, andINCONSISTENTdetermines whether it should be marked as undefined.Typical checkmark rendering:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_expander(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders an expander (as used in
GtkTreeViewandGtkExpander) in the area defined byx,y,width,height. The stateCHECKEDdetermines whether the expander is collapsed or expanded.Typical expander rendering:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_focus(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders a focus indicator on the rectangle determined by
x,y,width,height.Typical focus rendering:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_frame(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders a frame around the rectangle defined by
x,y,width,height.Examples of frame rendering, showing the effect of
border-image,border-color,border-width,border-radiusand junctions: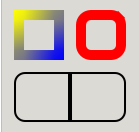
Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_handle(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders a handle (as in
GtkPanedandGtkWindow’s resize grip), in the rectangle determined byx,y,width,height.Handles rendered for the paned and grip classes:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- render_icon(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, texture: Texture, x: float, y: float) None
Renders the icon in
textureat the specifiedxandycoordinates.This function will render the icon in
textureat exactly its size, regardless of scaling factors, which may not be appropriate when drawing on displays with high pixel densities.Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_ttexture – a
GdkTexturecontaining the icon to drawx – X position for the
texturey – Y position for the
texture
- render_layout(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, layout: Layout) None
Renders
layouton the coordinatesx,yDeprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin
y – Y origin
layout – the
PangoLayoutto render
- render_line(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x0: float, y0: float, x1: float, y1: float) None
Renders a line from (x0, y0) to (x1, y1).
Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx0 – X coordinate for the origin of the line
y0 – Y coordinate for the origin of the line
x1 – X coordinate for the end of the line
y1 – Y coordinate for the end of the line
- render_option(context: StyleContext, cr: Context, x: float, y: float, width: float, height: float) None
Renders an option mark (as in a radio button), the
CHECKEDstate will determine whether the option is on or off, andINCONSISTENTwhether it should be marked as undefined.Typical option mark rendering:

Deprecated since version 4.10: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
context – a
GtkStyleContextcr – a
cairo_tx – X origin of the rectangle
y – Y origin of the rectangle
width – rectangle width
height – rectangle height
- rgb_to_hsv(r: float, g: float, b: float) tuple[float, float, float]
Converts a color from RGB space to HSV.
Input values must be in the [0.0, 1.0] range; output values will be in the same range.
- Parameters:
r – Red
g – Green
b – Blue
- set_debug_flags(flags: DebugFlags) None
Sets the GTK debug flags.
- Parameters:
flags – the debug flags to set
- show_uri(parent: Window | None, uri: str, timestamp: int) None
This function launches the default application for showing a given uri, or shows an error dialog if that fails.
- Parameters:
parent – parent window
uri – the uri to show
timestamp – timestamp from the event that triggered this call, or
``%GDK_CURRENT_TIME``
- show_uri_full(parent: Window | None, uri: str, timestamp: int, cancellable: Cancellable | None = None, callback: Callable[[...], None] | None = None, *user_data: Any) None
This function launches the default application for showing a given uri.
The
callbackwill be called when the launch is completed. It should callshow_uri_full_finish()to obtain the result.This is the recommended call to be used as it passes information necessary for sandbox helpers to parent their dialogs properly.
- Parameters:
parent – parent window
uri – the uri to show
timestamp – timestamp from the event that triggered this call, or
``%GDK_CURRENT_TIME``cancellable – a
GCancellableto cancel the launchcallback – a callback to call when the action is complete
user_data – data to pass to
callback
- show_uri_full_finish(parent: Window, result: AsyncResult) bool
Finishes the
show_uri()call and returns the result of the operation.Deprecated since version 4.10: Use
launch_finishorlaunch_finishinstead- Parameters:
parent – the
GtkWindowpassed toshow_uri()result –
GAsyncResultthat was passed tocallback
- Returns:
Trueif the URI was shown successfully. Otherwise,Falseis returned anderroris set
- test_accessible_assertion_message_role(domain: str, file: str, line: int, func: str, expr: str, accessible: Accessible, expected_role: AccessibleRole, actual_role: AccessibleRole) None
- Parameters:
domain
file
line
func
expr
accessible
expected_role
actual_role
- test_accessible_has_property(accessible: Accessible, property: AccessibleProperty) bool
Checks whether the
GtkAccessiblehaspropertyset.- Parameters:
accessible – a
GtkAccessibleproperty – a
GtkAccessibleProperty
- Returns:
Trueif thepropertyis set in theaccessible
- test_accessible_has_relation(accessible: Accessible, relation: AccessibleRelation) bool
Checks whether the
GtkAccessiblehasrelationset.- Parameters:
accessible – a
GtkAccessiblerelation – a
GtkAccessibleRelation
- Returns:
Trueif therelationis set in theaccessible
- test_accessible_has_role(accessible: Accessible, role: AccessibleRole) bool
Checks whether the
GtkAccessible:accessible-roleof the accessible isrole.- Parameters:
accessible – a
GtkAccessiblerole – a
GtkAccessibleRole
- Returns:
Trueif the role matches
- test_accessible_has_state(accessible: Accessible, state: AccessibleState) bool
Checks whether the
GtkAccessiblehasstateset.- Parameters:
accessible – a
GtkAccessiblestate – a
GtkAccessibleState
- Returns:
Trueif thestateis set in theaccessible
- test_list_all_types() list[type]
Return the type ids that have been registered after calling
test_register_all_types().- Returns:
0-terminated array of type ids
- test_register_all_types() None
Force registration of all core GTK object types.
This allows to refer to any of those object types via
type_from_name()after calling this function.
- test_widget_wait_for_draw(widget: Widget) None
Enters the main loop and waits for
widgetto be “drawn”.In this context that means it waits for the frame clock of
widgetto have run a full styling, layout and drawing cycle.This function is intended to be used for syncing with actions that depend on
widgetrelayouting or on interaction with the display server.- Parameters:
widget – the widget to wait for
- tree_create_row_drag_content(tree_model: TreeModel, path: TreePath) ContentProvider
Creates a content provider for dragging
pathfromtree_model.Deprecated since version 4.10: Use list models instead
- Parameters:
tree_model – a
GtkTreeModelpath – a row in
tree_model
- Returns:
a new
GdkContentProvider
- tree_get_row_drag_data(value: Any) tuple[bool, TreeModel, TreePath]
Obtains a
tree_modelandpathfrom value of target type%GTK_TYPE_TREE_ROW_DATA.The returned path must be freed with
free().Deprecated since version 4.10: Use list models instead
- Parameters:
value – a
GValue- Returns:
Trueifselection_datahad target type%GTK_TYPE_TREE_ROW_DATAis otherwise valid
- value_dup_expression(value: Any) Expression | None
Retrieves the
GtkExpressionstored inside the givenvalue, and acquires a reference to it.- Parameters:
value – a
GValueinitialized with typeGTK_TYPE_EXPRESSION- Returns:
a
GtkExpression
- value_get_expression(value: Any) Expression | None
Retrieves the
GtkExpressionstored inside the givenvalue.- Parameters:
value – a
GValueinitialized with typeGTK_TYPE_EXPRESSION- Returns:
a
GtkExpression
- value_set_expression(value: Any, expression: Expression) None
Stores the given
GtkExpressioninsidevalue.The
GValuewill acquire a reference to theexpression.- Parameters:
value – a
GValueinitialized with typeGTK_TYPE_EXPRESSIONexpression – a
GtkExpression
- value_take_expression(value: Any, expression: Expression | None = None) None
Stores the given
GtkExpressioninsidevalue.This function transfers the ownership of the
expressionto theGValue.- Parameters:
value – a
GValueinitialized with typeGTK_TYPE_EXPRESSIONexpression – a
GtkExpression