Functions
- attr_allow_breaks_new(allow_breaks: bool) Attribute
Create a new allow-breaks attribute.
If breaks are disabled, the range will be kept in a single run, as far as possible.
Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
allow_breaks –
Trueif we line breaks are allowed- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_background_alpha_new(alpha: int) Attribute
Create a new background alpha attribute.
Added in version 1.38.
- Parameters:
alpha – the alpha value, between 1 and 65536
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_background_new(red: int, green: int, blue: int) Attribute
Create a new background color attribute.
- Parameters:
red – the red value (ranging from 0 to 65535)
green – the green value
blue – the blue value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
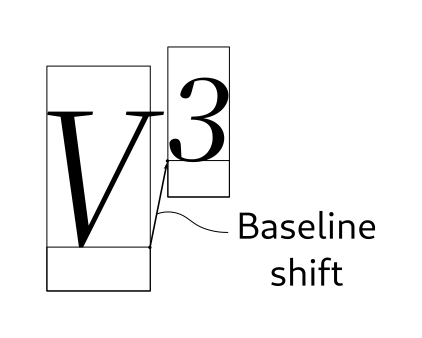
- attr_baseline_shift_new(shift: int) Attribute
Create a new baseline displacement attribute.
The effect of this attribute is to shift the baseline of a run, relative to the run of preceding run.
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
shift – either a
PangoBaselineShiftenumeration value or an absolute value (> 1024) in Pango units, relative to the baseline of the previous run. Positive values displace the text upwards.- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_break(text: str, length: int, attr_list: AttrList, offset: int, attrs: Sequence[LogAttr]) None
Apply customization from attributes to the breaks in
attrs.The line breaks are assumed to have been produced by
default_breakandtailor_break.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
text – text to break. Must be valid UTF-8
length – length of text in bytes (may be -1 if
textis nul-terminated)attr_list –
PangoAttrListto applyoffset – Byte offset of
textfrom the beginning of the paragraphattrs – array with one
PangoLogAttrper character intext, plus one extra, to be filled in
- attr_fallback_new(enable_fallback: bool) Attribute
Create a new font fallback attribute.
If fallback is disabled, characters will only be used from the closest matching font on the system. No fallback will be done to other fonts on the system that might contain the characters in the text.
Added in version 1.4.
- Parameters:
enable_fallback –
Trueif we should fall back on other fonts for characters the active font is missing- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_family_new(family: str) Attribute
Create a new font family attribute.
- Parameters:
family – the family or comma-separated list of families
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_font_desc_new(desc: FontDescription) Attribute
- Parameters:
desc
- attr_font_scale_new(scale: FontScale) Attribute
Create a new font scale attribute.
The effect of this attribute is to change the font size of a run, relative to the size of preceding run.
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
scale – a
PangoFontScalevalue, which indicates font size change relative to the size of the previous run.- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_foreground_alpha_new(alpha: int) Attribute
Create a new foreground alpha attribute.
Added in version 1.38.
- Parameters:
alpha – the alpha value, between 1 and 65536
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_foreground_new(red: int, green: int, blue: int) Attribute
Create a new foreground color attribute.
- Parameters:
red – the red value (ranging from 0 to 65535)
green – the green value
blue – the blue value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_gravity_hint_new(hint: GravityHint) Attribute
Create a new gravity hint attribute.
Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
hint – the gravity hint value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_gravity_new(gravity: Gravity) Attribute
Create a new gravity attribute.
Added in version 1.16.
- attr_insert_hyphens_new(insert_hyphens: bool) Attribute
Create a new insert-hyphens attribute.
Pango will insert hyphens when breaking lines in the middle of a word. This attribute can be used to suppress the hyphen.
Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
insert_hyphens –
Trueif hyphens should be inserted- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_letter_spacing_new(letter_spacing: int) Attribute
Create a new letter-spacing attribute.
Added in version 1.6.
- Parameters:
letter_spacing – amount of extra space to add between graphemes of the text, in Pango units
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_line_height_new(factor: float) Attribute
Modify the height of logical line extents by a factor.
This affects the values returned by
get_extents,get_pixel_extentsandget_line_extents.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
factor – the scaling factor to apply to the logical height
- attr_line_height_new_absolute(height: int) Attribute
Override the height of logical line extents to be
height.This affects the values returned by
get_extents,get_pixel_extentsandget_line_extents.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
height – the line height, in
SCALE-ths of a point
- attr_overline_color_new(red: int, green: int, blue: int) Attribute
Create a new overline color attribute.
This attribute modifies the color of overlines. If not set, overlines will use the foreground color.
Added in version 1.46.
- Parameters:
red – the red value (ranging from 0 to 65535)
green – the green value
blue – the blue value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_overline_new(overline: Overline) Attribute
Create a new overline-style attribute.
Added in version 1.46.
- Parameters:
overline – the overline style
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_rise_new(rise: int) Attribute
Create a new baseline displacement attribute.
- Parameters:
rise – the amount that the text should be displaced vertically, in Pango units. Positive values displace the text upwards.
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_scale_new(scale_factor: float) Attribute
Create a new font size scale attribute.
The base font for the affected text will have its size multiplied by
scale_factor.- Parameters:
scale_factor – factor to scale the font
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_sentence_new() Attribute
Marks the range of the attribute as a single sentence.
Note that this may require adjustments to word and sentence classification around the range.
Added in version 1.50.
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_shape_new(ink_rect: Rectangle, logical_rect: Rectangle) Attribute
- Parameters:
ink_rect
logical_rect
- attr_shape_new_with_data(ink_rect: Rectangle, logical_rect: Rectangle, data: None, copy_func: Callable[[...], None] | None = None, destroy_func: Callable[[None], None] | None = None) Attribute
- Parameters:
ink_rect
logical_rect
data
copy_func
destroy_func
- attr_show_new(flags: ShowFlags) Attribute
Create a new attribute that influences how invisible characters are rendered.
Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
flags –
PangoShowFlagsto apply- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_stretch_new(stretch: Stretch) Attribute
Create a new font stretch attribute.
- Parameters:
stretch – the stretch
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_strikethrough_color_new(red: int, green: int, blue: int) Attribute
Create a new strikethrough color attribute.
This attribute modifies the color of strikethrough lines. If not set, strikethrough lines will use the foreground color.
Added in version 1.8.
- Parameters:
red – the red value (ranging from 0 to 65535)
green – the green value
blue – the blue value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_strikethrough_new(strikethrough: bool) Attribute
Create a new strike-through attribute.
- Parameters:
strikethrough –
Trueif the text should be struck-through- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_style_new(style: Style) Attribute
Create a new font slant style attribute.
- Parameters:
style – the slant style
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_text_transform_new(transform: TextTransform) Attribute
Create a new attribute that influences how characters are transformed during shaping.
Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
transform –
PangoTextTransformto apply- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_underline_color_new(red: int, green: int, blue: int) Attribute
Create a new underline color attribute.
This attribute modifies the color of underlines. If not set, underlines will use the foreground color.
Added in version 1.8.
- Parameters:
red – the red value (ranging from 0 to 65535)
green – the green value
blue – the blue value
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_underline_new(underline: Underline) Attribute
Create a new underline-style attribute.
- Parameters:
underline – the underline style
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_variant_new(variant: Variant) Attribute
Create a new font variant attribute (normal or small caps).
- Parameters:
variant – the variant
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy.
- attr_weight_new(weight: Weight) Attribute
Create a new font weight attribute.
- Parameters:
weight – the weight
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- attr_word_new() Attribute
Marks the range of the attribute as a single word.
Note that this may require adjustments to word and sentence classification around the range.
Added in version 1.50.
- Returns:
the newly allocated
PangoAttribute, which should be freed withdestroy
- break_(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, attrs: Sequence[LogAttr]) None
- Parameters:
text
length
analysis
attrs
- default_break(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis | None, attrs: LogAttr, attrs_len: int) None
This is the default break algorithm.
It applies rules from the Unicode Line Breaking Algorithm without language-specific tailoring, therefore the
analyisargument is unused and can beNone.See
tailor_breakfor language-specific breaks.See
attr_breakfor attribute-based customization.- Parameters:
text – text to break. Must be valid UTF-8
length – length of text in bytes (may be -1 if
textis nul-terminated)analysis – a
PangoAnalysisstructure for thetextattrs – logical attributes to fill in
attrs_len – size of the array passed as
attrs
- extents_to_pixels(inclusive: Rectangle | None = None, nearest: Rectangle | None = None) None
Converts extents from Pango units to device units.
The conversion is done by dividing by the
SCALEfactor and performing rounding.The
inclusiverectangle is converted by flooring the x/y coordinates and extending width/height, such that the final rectangle completely includes the original rectangle.The
nearestrectangle is converted by rounding the coordinates of the rectangle to the nearest device unit (pixel).The rule to which argument to use is: if you want the resulting device-space rectangle to completely contain the original rectangle, pass it in as
inclusive. If you want two touching-but-not-overlapping rectangles stay touching-but-not-overlapping after rounding to device units, pass them in asnearest.Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
inclusive – rectangle to round to pixels inclusively
nearest – rectangle to round to nearest pixels
- find_base_dir(text: str, length: int) Direction
Searches a string the first character that has a strong direction, according to the Unicode bidirectional algorithm.
Added in version 1.4.
- Parameters:
text – the text to process. Must be valid UTF-8
length – length of
textin bytes (may be -1 iftextis nul-terminated)
- Returns:
The direction corresponding to the first strong character. If no such character is found, then
NEUTRALis returned.
- find_paragraph_boundary(text: str, length: int) tuple[int, int]
Locates a paragraph boundary in
text.A boundary is caused by delimiter characters, such as a newline, carriage return, carriage return-newline pair, or Unicode paragraph separator character.
The index of the run of delimiters is returned in
paragraph_delimiter_index. The index of the start of the next paragraph (index after all delimiters) is stored nnext_paragraph_start.If no delimiters are found, both
paragraph_delimiter_indexandnext_paragraph_startare filled with the length oftext(an index one off the end).- Parameters:
text – UTF-8 text
length – length of
textin bytes, or -1 if nul-terminated
- font_description_from_string(str: str) FontDescription
- Parameters:
str
- get_log_attrs(text: str, length: int, level: int, language: Language, attrs: Sequence[LogAttr]) None
Computes a
PangoLogAttrfor each character intext.The
attrsarray must have onePangoLogAttrfor each position intext; iftextcontains N characters, it has N+1 positions, including the last position at the end of the text.textshould be an entire paragraph; logical attributes can’t be computed without context (for example you need to see spaces on either side of a word to know the word is a word).- Parameters:
text – text to process. Must be valid UTF-8
length – length in bytes of
textlevel – embedding level, or -1 if unknown
language – language tag
attrs – array with one
PangoLogAttrper character intext, plus one extra, to be filled in
- get_mirror_char(ch: str, mirrored_ch: str) bool
Returns the mirrored character of a Unicode character.
Mirror characters are determined by the Unicode mirrored property.
Deprecated since version 1.30: Use
unichar_get_mirror_charinstead; the docs for that function provide full details.- Parameters:
ch – a Unicode character
mirrored_ch – location to store the mirrored character
- Returns:
Trueifchhas a mirrored character andmirrored_chis filled in,Falseotherwise
- gravity_get_for_script(script: Script, base_gravity: Gravity, hint: GravityHint) Gravity
- Parameters:
script
base_gravity
hint
- gravity_get_for_script_and_width(script: Script, wide: bool, base_gravity: Gravity, hint: GravityHint) Gravity
- Parameters:
script
wide
base_gravity
hint
- is_zero_width(ch: str) bool
Checks if a character that should not be normally rendered.
This includes all Unicode characters with “ZERO WIDTH” in their name, as well as bidi formatting characters, and a few other ones.
This is totally different from
unichar_iszerowidthand is at best misnamed.Added in version 1.10.
- Parameters:
ch – a Unicode character
- Returns:
Trueifchis a zero-width character,Falseotherwise
- itemize(context: Context, text: str, start_index: int, length: int, attrs: AttrList, cached_iter: AttrIterator | None = None) list[Item]
Breaks a piece of text into segments with consistent directional level and font.
Each byte of
textwill be contained in exactly one of the items in the returned list; the generated list of items will be in logical order (the start offsets of the items are ascending).cached_itershould be an iterator overattrscurrently positioned at a range before or containingstart_index;cached_iterwill be advanced to the range covering the position just afterstart_index+length. (i.e. if itemizing in a loop, just keep passing in the samecached_iter).- Parameters:
context – a structure holding information that affects the itemization process.
text – the text to itemize. Must be valid UTF-8
start_index – first byte in
textto processlength – the number of bytes (not characters) to process after
start_index. This must be >= 0.attrs – the set of attributes that apply to
text.cached_iter – Cached attribute iterator
- Returns:
a
GListofItemstructures. The items should be freed usingfreein combination withfree_full.
- itemize_with_base_dir(context: Context, base_dir: Direction, text: str, start_index: int, length: int, attrs: AttrList, cached_iter: AttrIterator | None = None) list[Item]
Like
:func:`~gi.repository.Pango.itemize`, but with an explicitly specified base direction.The base direction is used when computing bidirectional levels.
itemizegets the base direction from thePangoContext(seeset_base_dir).Added in version 1.4.
- Parameters:
context – a structure holding information that affects the itemization process.
base_dir – base direction to use for bidirectional processing
text – the text to itemize.
start_index – first byte in
textto processlength – the number of bytes (not characters) to process after
start_index. This must be >= 0.attrs – the set of attributes that apply to
text.cached_iter – Cached attribute iterator
- Returns:
a
GListofItemstructures. The items should be freed usingfreeprobably in combination withfree_full.
- log2vis_get_embedding_levels(text: str, length: int, pbase_dir: Direction) int
Return the bidirectional embedding levels of the input paragraph.
The bidirectional embedding levels are defined by the [Unicode Bidirectional Algorithm](http://www.unicode.org/reports/tr9/).
If the input base direction is a weak direction, the direction of the characters in the text will determine the final resolved direction.
Added in version 1.4.
- Parameters:
text – the text to itemize.
length – the number of bytes (not characters) to process, or -1 if
textis nul-terminated and the length should be calculated.pbase_dir – input base direction, and output resolved direction.
- Returns:
a newly allocated array of embedding levels, one item per character (not byte), that should be freed using
free.
- markup_parser_finish(context: MarkupParseContext) tuple[bool, AttrList, str, str]
Finishes parsing markup.
After feeding a Pango markup parser some data with
parse, use this function to get the list of attributes and text out of the markup. This function will not freecontext, usefreeto do so.Added in version 1.31.0.
- Parameters:
context – A valid parse context that was returned from
markup_parser_new- Returns:
Falseiferroris set, otherwiseTrue
- markup_parser_new(accel_marker: str) MarkupParseContext
Incrementally parses marked-up text to create a plain-text string and an attribute list.
See the Pango Markup docs for details about the supported markup.
If
accel_markeris nonzero, the given character will mark the character following it as an accelerator. For example,accel_markermight be an ampersand or underscore. All characters marked as an accelerator will receive aLOWattribute, and the first character so marked will be returned inaccel_char, when callingmarkup_parser_finish. Twoaccel_markercharacters following each other produce a single literalaccel_markercharacter.To feed markup to the parser, use
parseon the returnedMarkupParseContext. When done with feeding markup to the parser, usemarkup_parser_finishto get the data out of it, and then usefreeto free it.This function is designed for applications that read Pango markup from streams. To simply parse a string containing Pango markup, the
parse_markupAPI is recommended instead.Added in version 1.31.0.
- Parameters:
accel_marker – character that precedes an accelerator, or 0 for none
- Returns:
a
GMarkupParseContextthat should be destroyed withfree.
- parse_enum(type: type, str: str | None, warn: bool) tuple[bool, int, str]
Parses an enum type and stores the result in
value.If
strdoes not match the nick name of any of the possible values for the enum and is not an integer,Falseis returned, a warning is issued ifwarnisTrue, and a string representing the list of possible values is stored inpossible_values. The list is slash-separated, eg. “none/start/middle/end”.If failed and
possible_valuesis notNone, returned string should be freed usingfree().Added in version 1.16.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
type – enum type to parse, eg.
``%PANGO_TYPE_ELLIPSIZE_MODE``str – string to parse
warn – if
True, issue awarning()on bad input
- Returns:
Trueifstrwas successfully parsed
- parse_markup(markup_text: str, length: int, accel_marker: str) tuple[bool, AttrList, str, str]
Parses marked-up text to create a plain-text string and an attribute list.
See the Pango Markup docs for details about the supported markup.
If
accel_markeris nonzero, the given character will mark the character following it as an accelerator. For example,accel_markermight be an ampersand or underscore. All characters marked as an accelerator will receive aLOWattribute, and the first character so marked will be returned inaccel_char. Twoaccel_markercharacters following each other produce a single literalaccel_markercharacter.To parse a stream of pango markup incrementally, use
markup_parser_new.If any error happens, none of the output arguments are touched except for
error.- Parameters:
markup_text –
markup to parse (see the Pango Markup docs)
length – length of
markup_text, or -1 if nul-terminatedaccel_marker – character that precedes an accelerator, or 0 for none
- Returns:
Falseiferroris set, otherwiseTrue
- parse_stretch(str: str, warn: bool) tuple[bool, Stretch]
Parses a font stretch.
The allowed values are “ultra_condensed”, “extra_condensed”, “condensed”, “semi_condensed”, “normal”, “semi_expanded”, “expanded”, “extra_expanded” and “ultra_expanded”. Case variations are ignored and the ‘_’ characters may be omitted.
- Parameters:
str – a string to parse.
warn – if
True, issue awarning()on bad input.
- Returns:
Trueifstrwas successfully parsed.
- parse_style(str: str, warn: bool) tuple[bool, Style]
Parses a font style.
The allowed values are “normal”, “italic” and “oblique”, case variations being ignored.
- Parameters:
str – a string to parse.
warn – if
True, issue awarning()on bad input.
- Returns:
Trueifstrwas successfully parsed.
- parse_variant(str: str, warn: bool) tuple[bool, Variant]
Parses a font variant.
The allowed values are “normal”, “small-caps”, “all-small-caps”, “petite-caps”, “all-petite-caps”, “unicase” and “title-caps”, case variations being ignored.
- Parameters:
str – a string to parse.
warn – if
True, issue awarning()on bad input.
- Returns:
Trueifstrwas successfully parsed.
- parse_weight(str: str, warn: bool) tuple[bool, Weight]
Parses a font weight.
The allowed values are “heavy”, “ultrabold”, “bold”, “normal”, “light”, “ultraleight” and integers. Case variations are ignored.
- Parameters:
str – a string to parse.
warn – if
True, issue awarning()on bad input.
- Returns:
Trueifstrwas successfully parsed.
- quantize_line_geometry() tuple[int, int]
Quantizes the thickness and position of a line to whole device pixels.
This is typically used for underline or strikethrough. The purpose of this function is to avoid such lines looking blurry.
Care is taken to make sure
thicknessis at least one pixel when this function returns, but returnedpositionmay become zero as a result of rounding.Added in version 1.12.
- read_line(stream: None, str: String) int
Reads an entire line from a file into a buffer.
Lines may be delimited with ‘n’, ‘r’, ‘nr’, or ‘rn’. The delimiter is not written into the buffer. Text after a ‘#’ character is treated as a comment and skipped. ‘' can be used to escape a # character. ‘' proceeding a line delimiter combines adjacent lines. A ‘' proceeding any other character is ignored and written into the output buffer unmodified.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
stream – a stdio stream
str –
GStringbuffer into which to write the result
- Returns:
0 if the stream was already at an
%EOFcharacter, otherwise the number of lines read (this is useful for maintaining a line number counter which doesn’t combine lines with ‘')
- reorder_items(items: list[Item]) list[Item]
Reorder items from logical order to visual order.
The visual order is determined from the associated directional levels of the items. The original list is unmodified.
- (Please open a bug if you use this function.
It is not a particularly convenient interface, and the code is duplicated elsewhere in Pango for that reason.)
- Parameters:
items – a
GListofPangoItemin logical order.- Returns:
a
GListofPangoItemstructures in visual order.
- scan_int() tuple[bool, str, int]
Scans an integer.
Leading white space is skipped.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Returns:
Falseif a parse error occurred
- scan_string(out: String) tuple[bool, str]
Scans a string into a
GStringbuffer.The string may either be a sequence of non-white-space characters, or a quoted string with ‘”’. Instead a quoted string, ‘"’ represents a literal quote. Leading white space outside of quotes is skipped.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
out – a
GStringinto which to write the result- Returns:
Falseif a parse error occurred
- scan_word(out: String) tuple[bool, str]
Scans a word into a
GStringbuffer.A word consists of [A-Za-
z_] followed by zero or more [A-Za-z_0-9]. Leading white space is skipped.Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
out – a
GStringinto which to write the result- Returns:
Falseif a parse error occurred
- shape(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, glyphs: GlyphString) None
Convert the characters in
textinto glyphs.Given a segment of text and the corresponding
PangoAnalysisstructure returned fromitemize, convert the characters into glyphs. You may also pass in only a substring of the item fromitemize.It is recommended that you use
shape_fullinstead, since that API allows for shaping interaction happening across text item boundaries.Some aspects of hyphen insertion and text transformation (in particular, capitalization) require log attrs, and thus can only be handled by
shape_item.Note that the extra attributes in the
analyisthat is returned fromitemizehave indices that are relative to the entire paragraph, so you need to subtract the item offset from their indices before callingshape.- Parameters:
text – the text to process
length – the length (in bytes) of
textanalysis –
PangoAnalysisstructure fromitemizeglyphs – glyph string in which to store results
- shape_full(item_text: str, item_length: int, paragraph_text: str | None, paragraph_length: int, analysis: Analysis, glyphs: GlyphString) None
Convert the characters in
textinto glyphs.Given a segment of text and the corresponding
PangoAnalysisstructure returned fromitemize, convert the characters into glyphs. You may also pass in only a substring of the item fromitemize.This is similar to
shape, except it also can optionally take the full paragraph text as input, which will then be used to perform certain cross-item shaping interactions. If you have access to the broader text of whichitem_textis part of, provide the broader text asparagraph_text. Ifparagraph_textisNone, item text is used instead.Some aspects of hyphen insertion and text transformation (in particular, capitalization) require log attrs, and thus can only be handled by
shape_item.Note that the extra attributes in the
analyisthat is returned fromitemizehave indices that are relative to the entire paragraph, so you do not pass the full paragraph text asparagraph_text, you need to subtract the item offset from their indices before callingshape_full.Added in version 1.32.
- Parameters:
item_text – valid UTF-8 text to shape.
item_length – the length (in bytes) of
item_text. -1 means nul-terminated text.paragraph_text – text of the paragraph (see details).
paragraph_length – the length (in bytes) of
paragraph_text. -1 means nul-terminated text.analysis –
PangoAnalysisstructure fromitemize.glyphs – glyph string in which to store results.
- shape_item(item: Item, paragraph_text: str | None, paragraph_length: int, log_attrs: LogAttr | None, glyphs: GlyphString, flags: ShapeFlags) None
Convert the characters in
iteminto glyphs.This is similar to
shape_with_flags, except it takes aPangoIteminstead of separateitem_textandanalysisarguments.It also takes
log_attrs, which are needed for implementing some aspects of hyphen insertion and text transforms (in particular, capitalization).Note that the extra attributes in the
analyisthat is returned fromitemizehave indices that are relative to the entire paragraph, so you do not pass the full paragraph text asparagraph_text, you need to subtract the item offset from their indices before callingshape_with_flags.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
item –
PangoItemto shapeparagraph_text – text of the paragraph (see details).
paragraph_length –
the length (in bytes) of
paragraph_text.-1 means nul-terminated text.
log_attrs – array of
PangoLogAttrforitemglyphs – glyph string in which to store results
flags – flags influencing the shaping process
- shape_with_flags(item_text: str, item_length: int, paragraph_text: str | None, paragraph_length: int, analysis: Analysis, glyphs: GlyphString, flags: ShapeFlags) None
Convert the characters in
textinto glyphs.Given a segment of text and the corresponding
PangoAnalysisstructure returned fromitemize, convert the characters into glyphs. You may also pass in only a substring of the item fromitemize.This is similar to
shape_full, except it also takes flags that can influence the shaping process.Some aspects of hyphen insertion and text transformation (in particular, capitalization) require log attrs, and thus can only be handled by
shape_item.Note that the extra attributes in the
analyisthat is returned fromitemizehave indices that are relative to the entire paragraph, so you do not pass the full paragraph text asparagraph_text, you need to subtract the item offset from their indices before callingshape_with_flags.Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
item_text – valid UTF-8 text to shape
item_length –
the length (in bytes) of
item_text.-1 means nul-terminated text.
paragraph_text – text of the paragraph (see details).
paragraph_length –
the length (in bytes) of
paragraph_text.-1 means nul-terminated text.
analysis –
PangoAnalysisstructure fromitemizeglyphs – glyph string in which to store results
flags – flags influencing the shaping process
- skip_space() tuple[bool, str]
Skips 0 or more characters of white space.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Returns:
Falseif skipping the white space leaves the position at a ‘0’ character.
- split_file_list(str: str) list[str]
Splits a
%G_SEARCHPATH_SEPARATOR-separated list of files, stripping white space and substituting ~/ with $HOME/.Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
str – a
``%G_SEARCHPATH_SEPARATOR``separated list of filenames- Returns:
a list of strings to be freed with
strfreev()
- tailor_break(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, offset: int, attrs: Sequence[LogAttr]) None
Apply language-specific tailoring to the breaks in
attrs.The line breaks are assumed to have been produced by
default_break.If
offsetis not -1, it is used to apply attributes fromanalysisthat are relevant to line breaking.Note that it is better to pass -1 for
offsetand useattr_breakto apply attributes to the whole paragraph.Added in version 1.44.
- Parameters:
text – text to process. Must be valid UTF-8
length – length in bytes of
textanalysis –
PangoAnalysisfortextoffset – Byte offset of
textfrom the beginning of the paragraph, or -1 to ignore attributes fromanalysisattrs – array with one
PangoLogAttrper character intext, plus one extra, to be filled in
- trim_string(str: str) str
Trims leading and trailing whitespace from a string.
Deprecated since version 1.38: Please do not use it in newly written code
- Parameters:
str – a string
- Returns:
A newly-allocated string that must be freed with
free()
- unichar_direction(ch: str) Direction
Determines the inherent direction of a character.
The inherent direction is either
PANGO_DIRECTION_LTR,PANGO_DIRECTION_RTL, orPANGO_DIRECTION_NEUTRAL.This function is useful to categorize characters into left-to-right letters, right-to-left letters, and everything else. If full Unicode bidirectional type of a character is needed,
for_unicharcan be used instead.- Parameters:
ch – a Unicode character
- Returns:
the direction of the character.
- units_from_double(d: float) int
Converts a floating-point number to Pango units.
The conversion is done by multiplying
dbySCALEand rounding the result to nearest integer.Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
d – double floating-point value
- Returns:
the value in Pango units.
- units_to_double(i: int) float
Converts a number in Pango units to floating-point.
The conversion is done by dividing
ibySCALE.Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
i – value in Pango units
- Returns:
the double value.
- version() int
Returns the encoded version of Pango available at run-time.
This is similar to the macro
%PANGO_VERSIONexcept that the macro returns the encoded version available at compile-time. A version number can be encoded into an integer usingVERSION_ENCODE().Added in version 1.16.
- Returns:
The encoded version of Pango library available at run time.
- version_check(required_major: int, required_minor: int, required_micro: int) str | None
Checks that the Pango library in use is compatible with the given version.
Generally you would pass in the constants
VERSION_MAJOR,VERSION_MINOR,VERSION_MICROas the three arguments to this function; that produces a check that the library in use at run-time is compatible with the version of Pango the application or module was compiled against.Compatibility is defined by two things: first the version of the running library is newer than the version
required_major.required_minor.``required_micro``. Second the running library must be binary compatible with the versionrequired_major.required_minor.``required_micro`` (same major version.)For compile-time version checking use
VERSION_CHECK().Added in version 1.16.
- Parameters:
required_major – the required major version
required_minor – the required minor version
required_micro – the required major version
- Returns:
Noneif the Pango library is compatible with the given version, or a string describing the version mismatch. The returned string is owned by Pango and should not be modified or freed.
- version_string() str
Returns the version of Pango available at run-time.
This is similar to the macro
VERSION_STRINGexcept that the macro returns the version available at compile-time.Added in version 1.16.
- Returns:
A string containing the version of Pango library available at run time. The returned string is owned by Pango and should not be modified or freed.