GlyphString
- class GlyphString(**kwargs)
A PangoGlyphString is used to store strings of glyphs with geometry
and visual attribute information.
The storage for the glyph information is owned by the structure which simplifies memory management.
Constructors
- class GlyphString
- classmethod new() GlyphString
Create a new
PangoGlyphString.
Methods
- class GlyphString
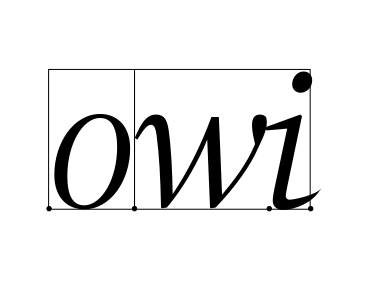
- extents(font: Font) tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]
Compute the logical and ink extents of a glyph string.
See the documentation for
get_glyph_extentsfor details about the interpretation of the rectangles.Examples of logical (red) and ink (green) rects:


- Parameters:
font – a
PangoFont
- extents_range(start: int, end: int, font: Font) tuple[Rectangle, Rectangle]
Computes the extents of a sub-portion of a glyph string.
The extents are relative to the start of the glyph string range (the origin of their coordinate system is at the start of the range, not at the start of the entire glyph string).
- Parameters:
start – start index
end – end index (the range is the set of bytes with indices such that start <= index < end)
font – a
PangoFont
- get_logical_widths(text: str, length: int, embedding_level: int, logical_widths: Sequence[int]) None
Given a
PangoGlyphStringand corresponding text, determine the width corresponding to each character.When multiple characters compose a single cluster, the width of the entire cluster is divided equally among the characters.
See also
get_logical_widths.- Parameters:
text – the text corresponding to the glyphs
length – the length of
text, in bytesembedding_level – the embedding level of the string
logical_widths – an array whose length is the number of characters in text (equal to
g_utf8_strlen (text, length)unless text hasNULbytes) to be filled in with the resulting character widths.
- get_width() int
Computes the logical width of the glyph string.
This can also be computed using
extents. However, since this only computes the width, it’s much faster. This is in fact only a convenience function that computes the sum ofgeometry.width for each glyph in theglyphs.Added in version 1.14.
- index_to_x(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, index_: int, trailing: bool) int
Converts from character position to x position.
The X position is measured from the left edge of the run. Character positions are obtained using font metrics for ligatures where available, and computed by dividing up each cluster into equal portions, otherwise.
- Parameters:
text – the text for the run
length – the number of bytes (not characters) in
text.analysis – the analysis information return from
itemizeindex – the byte index within
texttrailing – whether we should compute the result for the beginning (
False) or end (True) of the character.
- index_to_x_full(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, attrs: LogAttr | None, index_: int, trailing: bool) int
Converts from character position to x position.
This variant of
index_to_xadditionally accepts aPangoLogAttrarray. The grapheme boundary information in it can be used to disambiguate positioning inside some complex clusters.Added in version 1.50.
- Parameters:
text – the text for the run
length – the number of bytes (not characters) in
text.analysis – the analysis information return from
itemizeattrs –
PangoLogAttrarray fortextindex – the byte index within
texttrailing – whether we should compute the result for the beginning (
False) or end (True) of the character.
- set_size(new_len: int) None
Resize a glyph string to the given length.
- Parameters:
new_len – the new length of the string
- x_to_index(text: str, length: int, analysis: Analysis, x_pos: int) tuple[int, int]
Convert from x offset to character position.
Character positions are computed by dividing up each cluster into equal portions. In scripts where positioning within a cluster is not allowed (such as Thai), the returned value may not be a valid cursor position; the caller must combine the result with the logical attributes for the text to compute the valid cursor position.
- Parameters:
text – the text for the run
length – the number of bytes (not characters) in text.
analysis – the analysis information return from
itemizex_pos – the x offset (in Pango units)